BRA Day is an initiative designed to promote education, awareness and access for women who may wish to consider post-mastectomy breast reconstruction.
Skin Cancer
More than one in four fair-skinned caucasians will get a skin cancer in their lifetime. Plastic surgeons are involved in removing a large share of these as most occur on the “sun belt” of the face, which includes the nose, the cheeks, the temples and the ears.
Who is susceptible?
Anyone who sunburns can get skin cancer; this includes aging people, who are more susceptible to skin cancer. As we age, our DNA repair enzymes are less able to reverse damage caused by ultraviolet light . In other words, the older you are when you get sunburned, the more likely you are to get a skin cancer from the sunburn.
Treat skin cancer early
The longer you wait to have a skin cancer removed, the bigger it gets, and the more complicated the reconstruction becomes to return the patient to their normal state. This is why it is best treated early while it is still small.
Types of skin cancer
Basal cell skin cancer
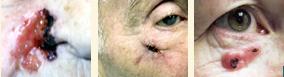 Basal cell skin cancer is the most common kind of skin cancer. It usually presents as a raised red nodule with a central ulcer.
Basal cell skin cancer is the most common kind of skin cancer. It usually presents as a raised red nodule with a central ulcer.
Basal cell skin cancer never goes away. These cancers generally do not spread elsewhere (metastasize), which is good. However, because they can grow locally, it is best to remove them early when they are small.
The cure rate with surgical removal is over 95%. Some patients require more than one operation to remove the entire lesion.
Squamous cell skin cancer
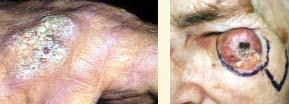 This type of skin cancer looks like basal cell skin cancer, but the red areas tend to have hard rough spots on them and bleed more easily.
This type of skin cancer looks like basal cell skin cancer, but the red areas tend to have hard rough spots on them and bleed more easily.
Squamous cell skin cancers have a slightly higher risk of metastasizing than basal cell skin cancers. However, the risk of metastasis and death is usually less than 5% if the squamous cell skin cancer is in a sun-induced area (i.e., not on the genitals, inside the mouth or in the anal areas).
Treatment again involves surgical removal.
Malignant melanoma
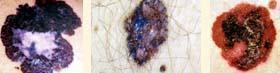 Malignant melanoma occurs in 1% of fair-skinned caucasians. This kind of cancer does metastasize and is the most serious of the skin cancers. However, if caught early and removed, the cure rate is high.
Malignant melanoma occurs in 1% of fair-skinned caucasians. This kind of cancer does metastasize and is the most serious of the skin cancers. However, if caught early and removed, the cure rate is high.
Three things make melanoma obvious, as this is not a subtle skin cancer in most instances:
- Melanoma is usually black or has black in it, and arises from moles 1/3 of the time
- Melanoma tends to grow quickly and will often double in size over weeks
- Melanoma tends to have an unusual shape such as the shape of Newfoundland or Prince Edward Island, as opposed to benign moles, which are usually round or oval.
The treatment of melanoma may involve an Oncology team that includes a Plastic surgeon. Diagnostic tests will be done to ensure it has not spread anywhere. The team will discuss the best treatment option for you.
